Technical


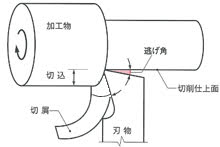
Compressed solid Fluorocarbon material goes through a machining process to become the final product.
At this process, it is very important to understand the features of PTFE.
PTFE is a thermoplastic resin that has a melting point around 340℃ at the unfired state, and 327 ℃ at the fired molded state.
When the temperature of the preform material is raised above the melting point, it changes to a transparent color.
In this state, the material is elastic but it does not liquidize, so after the compression molding process, it must go through the machining process.
PTFE has flexibility, elasticity, low thermal conductivity and high coefficient of thermal expansion. At around 20 ℃, its volume change around 1% to 2%, so special care is required at the time of processing.
The tolerance after machining tolerance varies with processing method and size. The processing accuracy mainly influenced by the tool used, the resin's residual stress and the molding method. If higher dimensional accuracy is required, after some rough processing, the material is heated to a high temperature to be annealed and then it goes through the machining process.
We are experienced at processing Fluorocarbon resin such as PTFE, PFA and also engineering plastics such as Vespel, PEEK, POM, etc.
Features of machining
 Compared to injection molding:
Compared to injection molding:
・Products of uneven thickness can be manufactured.
・It is suitable for small lots.
・It can manufacture products with higher accuracy.
Property data of PTFE
Examples of usage and application
Machining can achieve high uniformity and high accuracy.
It is suitable for processing materials such as diaphragm or bellows
 |
 |
| Bellows (cross section) thickness: 0.8mm |
Bellows (cross section) thickness: 0.4mm |
 |
 |
| Diaphragm thickness |
Diaphragm (cross section) thickness: 0.5mm |







